File : contiguous logical address
ㄴ type : Data / Program + text/source...
ㄴ 추상 데이터 타입, 여러 명령어 존재
ㄴ create, open, write..
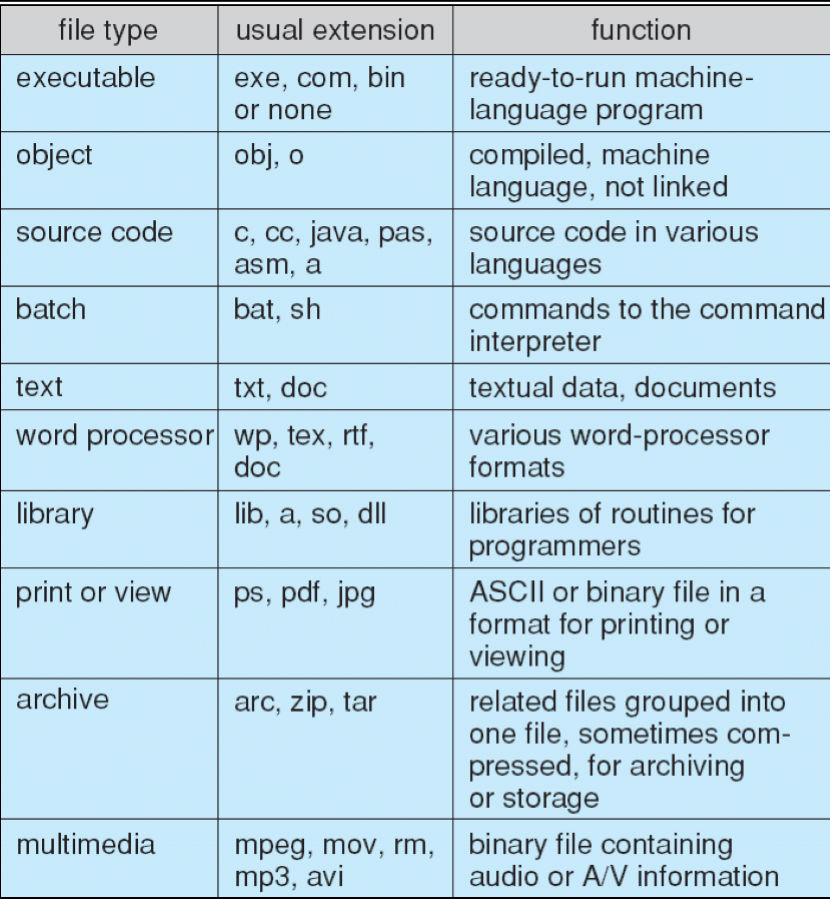
Open File : 열려있는 파일관리 ㄴ table , pointer,count 등 이용
Open File locking
ㄴ shared: Read 공유 / execlusive : only1 process Write
ㄴ mandatory: request -> 승인OK -> access / advisory : Lock 확인 -> access 선택
sequential-access
: 한쪽방향으로 pointer 증가
ㄴ Rewrite X -> rewind(reset) 후에 write
Direct access
ㄴ file들을 고정된 크기로

ㄴ n: block number
ㄴ n번째로 direct접근
Index/relative Files

index : 메모리에 있음 -> 찾는 속도 빠름

Directory : many Files 묶음
Single-level directory
ㄴ 1개의 디렉토리에 all files
ㄴ 같은이름 + grouping X
>>
Two-level directory
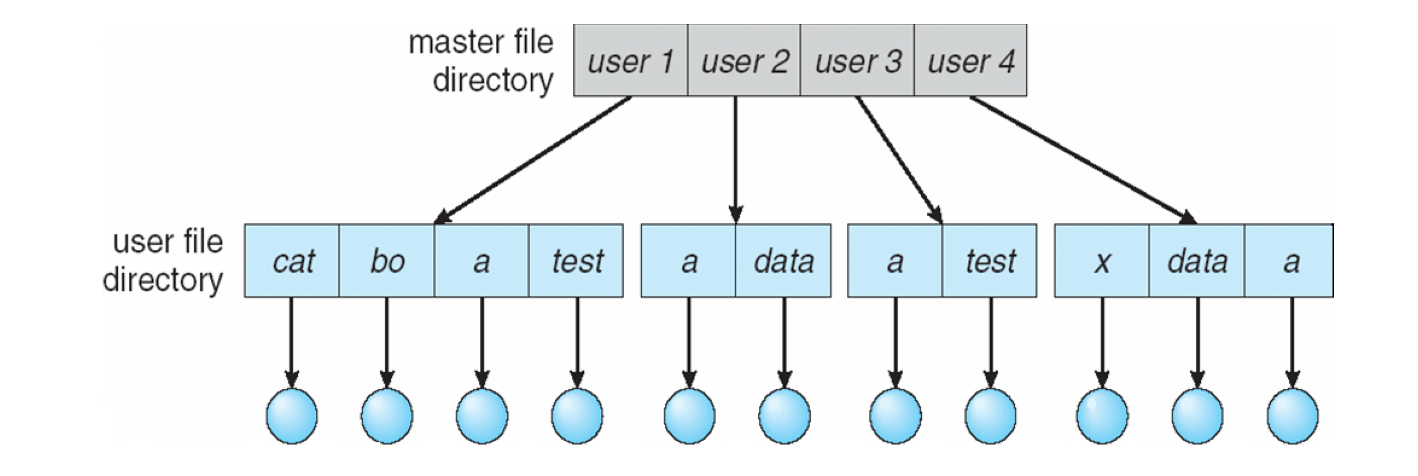
ㄴ 같은이름O / grouping X
ㄴ 고양이 이라는 거에 하나의 file 만 가능함
Tree-structed
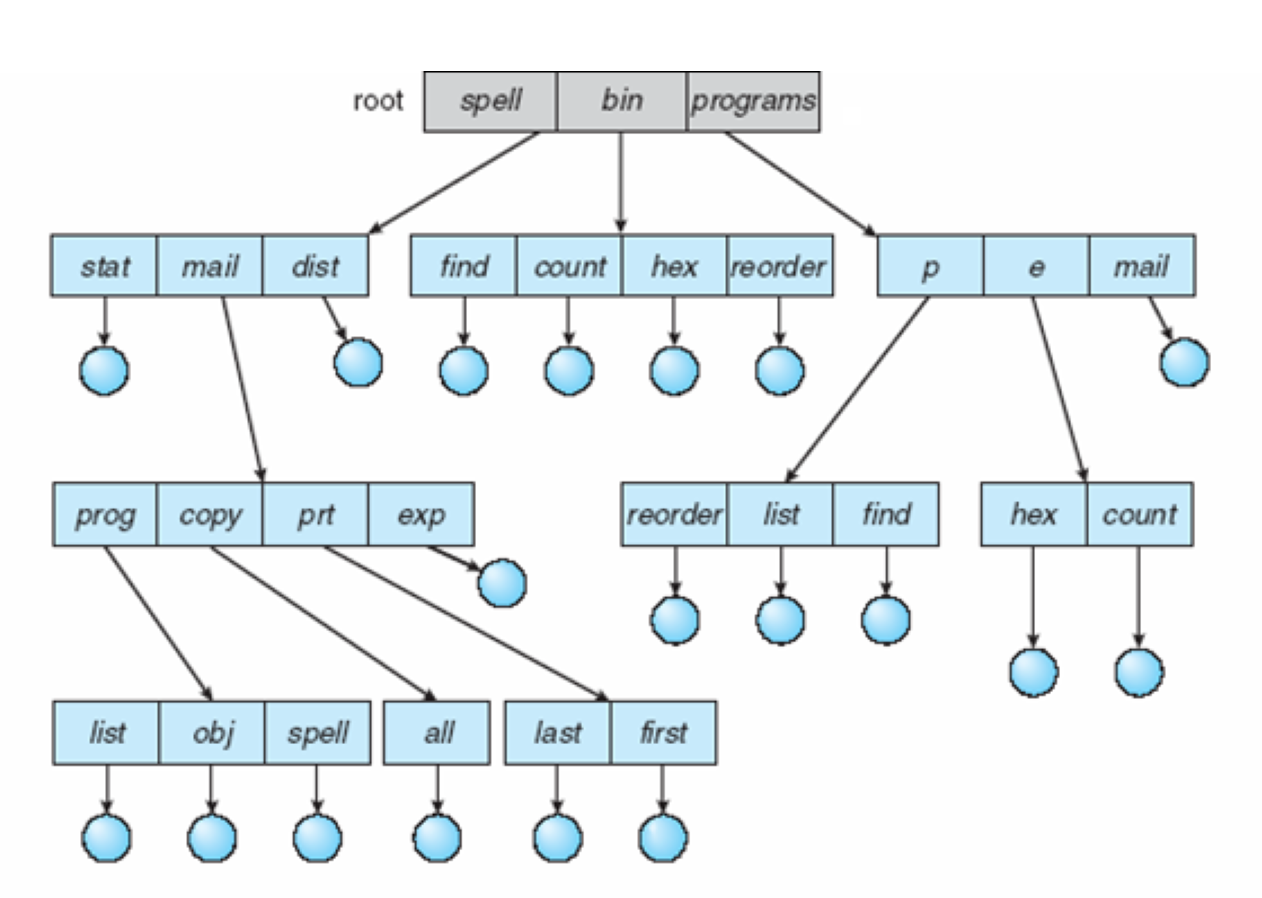
ㄴ grouping O
ㄴ mail이라는거에 prog/copy/prt/exp... 가능
ㄴ Absolute: 전체 경로 / relative : 현재 file 기준
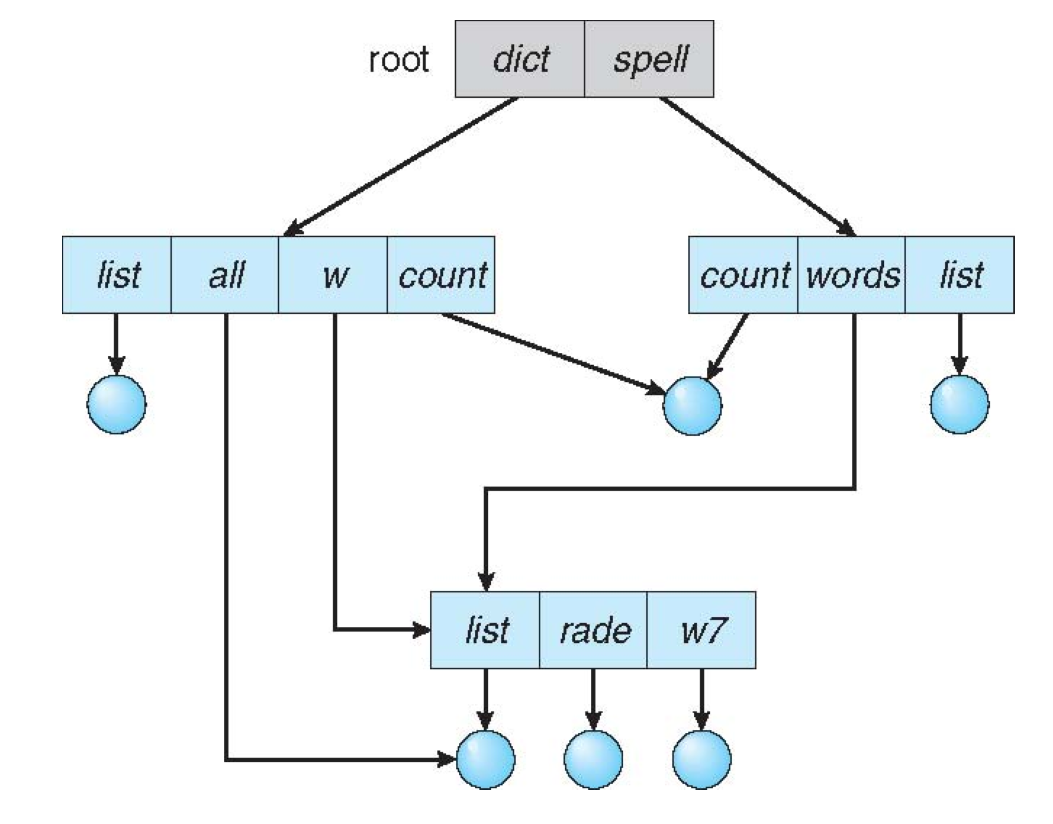
문제1) Aliasing : 하나에 두개의 이름을 가짐 list,all + w,words -> list
문제2) dangling pointer: count 디렉토리에서 같은 file을 공유함
if) 왼쪽 count에서 삭제시 -> 우측 count에서 문제발생!
>>
해결1) BackPointer : pointer 추적 -> 왼쪽 삭제시 우측도 같이 제거
해결2) Entry-hold-count solution : count 0 일시 제거
ㄴif) 좌측 우측 2개-> count 2
해결3) Link(hard) : 기존
ㄴ resolve the link(soft)
ㄴ B -> A -> file() : 간접적으로
General Graph

ㄴ cycle 존재 -> 무한 loop
ㄴ garbage collection : 더 이상 참조X -> 제거하는 알고리즘
ㄴ new link 할 때마다 cycle 확인
File Protection
: Access lists and group

ㄴ 111 110 001
RWX RW X
(root) (group) (pubile)
File structure
ㄴ File system in Disk
ㄴ interface / logical -> physical address mapping
ㄴ 효율적이고 편리한 접근 제공
ㄴ File control bolck(FCB): 파일에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 저장 구조
ㄴ Device driver : 물리적 장치를 제어
File system layerd
// many File system in OS // CD,DVD,Blue-Ray...
ㄴ 장) 복잡성 / 중복성 ↓
ㄴ 단) Overhead

Logical file system: metadata관리 // FCB + protection
File organization module: 파일, logical address , 물리 block의 관계를 이해
ㄴ logical block number -> physical , Disk 여유 공간 관리/ 할당
Basic file system: "블록 123을 가져오라" 받은 명령 -> Device driver 로 전달
+ memory buffer / cache관리 // 할당, 해제, 교체
buffer <> cache
// buffer : 전송 중인 데이터를 임시 보관
// cache : 자주 사용되는 데이터 임시 보관
Device drivers: I/O control 계층 -> I/O 장치 관리
ㄴ High 명령 -> low 명령 변환 // HW controller가 이해
// "드라이브1, 실린더 72, 트랙 2, 섹터 10 -> 메모리 위치 1060으로 읽어라" // 상위 명령, USER가 이해
File-System operations ON Disk
- Boot control block: OS boot 정보 // 볼륨의 첫 번째 블록
- Volume control bloc 볼륨의 상세 정보
- Directory structure: 파일 이름 / inode 번호(MFT) 관리
- NTFS : FCB들을 하나로 // 관계형 DB -> MFT(master file table) 내에 저장
File system data struct IN Memory
- Mount table: mounted File system 정보
- System-wide open-file table: In system, All FCBs
- Per-process open-file table: 각 프로세스별 FCBs
- buff : Data block in Disk 임시 저장
- open() : File handler return
- read() : Data -> Memory
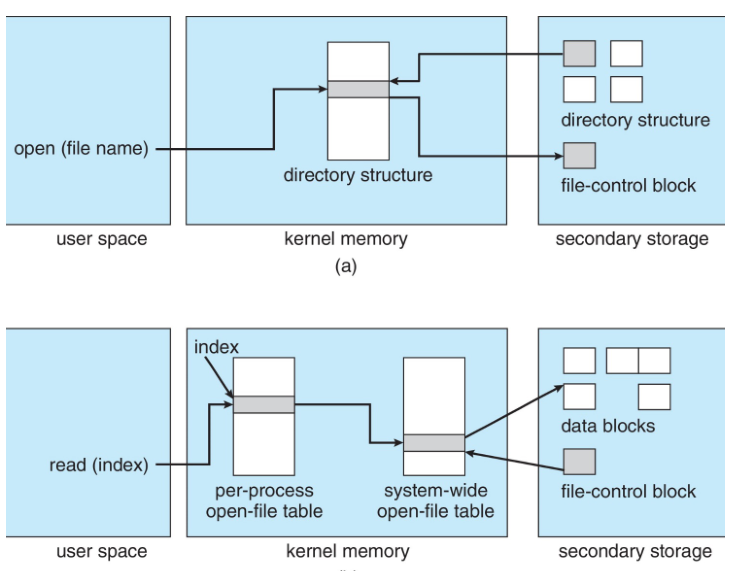
1. open() : directory structre -> FCB -> System-wide 에 복사
ㄴ Per-process -> system -wide(복사해둔 FCB가있는곳)를 가르킴
ㄴ File handler return
2. read() : 포인터 참고 -> 실제 Disk에있는 block에 접근 -> buffer로 전달
Directory Implementation(구현)
Linear list 파일 이름과 데이터 블록 포인터를 순차적인 리스트로 관리합니다.
ㄴ 간단 <> linear search -> time ↑
>> linked / DB) B+ tree
Hash Table: hash fuction -> file name을 hash값(index)로 변환 -> Directory 정보로 저장
ㄴ search time↓ <> Collisions: 다른 file name -> 같은 해시 값으로 매핑
>> chained-overflow
Allocation Methods
1. Contiguous

count 0 부터 2개 -> 0,1 // continguous
ㄴ 간단 <> external fragmentation
>> compaction -> 성능↓
LA : logical address ÷ block size(ex) 512B)
Q : block num
R : offset // 해당 block 內
>> physical block address = 시작 주소 + Q1.1 Extent-Based Systems : 1.+ block 을 여러개로 묶어서 // ex) 1~10MB
2. Linked

ㄴ external fragmentation X <> internal O
ㄴ Linked의 고질적 단점 : 하나씩 search time↑
> 10개 block 단위로 cluster -> linked 길의↓
<> internal ↑↑
ㄴ 신뢰성↓ : 앞의 포인터 하나 손상시 다음 포인터를 믿을수 있느냐?
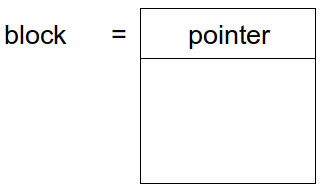
LA/(blcok size - pointer size)
// 사진은 pointer size가 1이라 가정
offset : R+1 // 사진 처럼 Base에 포인터 1을 보정
2-2 FAT : File-Allocation Table

like page table 처럼 test :217 -> 618 -> 339... Liked
3. Indexed Allocation
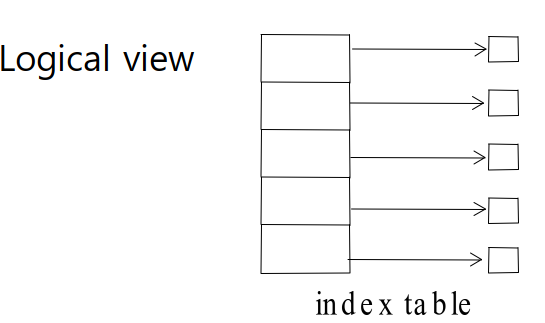
ㄴ 각각 쪼개서 number 들을 하나의 index table(block) 으로 만듦

단) index block (ex) 19 -> 자체가 overhead

511 : pointer 보정 -1
Q1 : 어느 index table인지
Q2 : index table의 offset // block 내 몇번째 block number인지
R2 : blcok offset
Two-level index
: 4KB / per 1-block : 4B짜리 pointer -> 1024개
ㄴ 1개의 outer/inner block : 1024개의 pointer
ㄴ 1024 * 1024 = 1M개의 Data block pointer
>>> 1M * 각 4KB = 4GB 의 파일 표현 가능

'전공 > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| File system -2 (1) | 2025.06.07 |
|---|---|
| I/O systems (0) | 2025.06.05 |
| Virtual memory-2 (0) | 2025.05.23 |
| 가상메모리 (0) | 2025.05.15 |
| 메모리-4 (0) | 2025.05.11 |