bootstrap program (bootloader) ~= firmware
: in ( ROM, EPROM) > 시스템 초기화, kenel 을 메모리에 올림
+
kernel
: 항상돌아가는 1개의 program
+
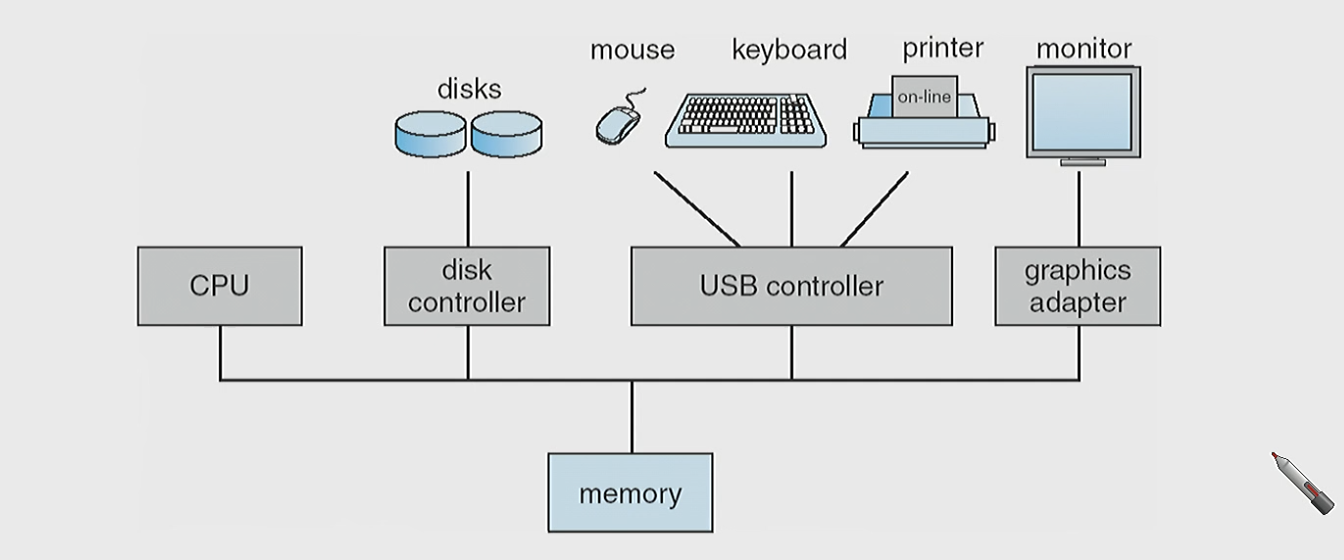
divice: interrupt 발생! > loacal buffer > I/O : divice,localbuffer control > CPU : main memory로 move
// DMA 사용시에는 바로 메모리로 (CPU X)
<> software Interrupt : Command ( user -> privileged 모드변경)
<> Exception : CPU내부에서 발생 (divide by Zero)
>>>

OS
1. 유저 인터페이스 : GUI, Batch
2. 프로그램 execution : 시스템 -> 프로그램 메모리에 load
3. I/O 장치 운영
4. File-system 조작
5. communication : 메모리공유, 메세지 전송
6. 에러감지 -> 적절한 action
7. Resource 할당 : 메모리 관리 (CPU, 메인메모리,저장장치)
8. Accounting : user1,2,3 ... 관리
9. 보호/보안
protection : Resource is controlled 을 잘못 접근하는것으로부터
security : 외부, I/O 로부터의 악의적인 접근으로부터
// 시스템의 보안정도는 system chain 에서 가장 약한 부분이다.


PCB : process(task) control block
> 프로세스 정보관리 자료구조
>
PID, process state, PC(program counter) : 다음 실행할 명령어의 주소
register, scheduling information(우선순위, queue)
memory, Accounting(얼만큼,얼마나 할지), I/O state information +file
Linux PCB : task_struct
> current : 현재 실행 task_struct + 링크드리스트로 다음/이전 프로세스까지
process scheduler : ready queue 에있는 T들 스케쥴링
// 옛날에는 PCB <> 요즘엔 기술up : TCB

각 state(wait ,ready,running,,) 마다 queue(PCBs)
1 Process(Thread) 가 스케쥴러에의해 state 이동 -> queue 들에 PCB(TCB)를 넣으며 옮겨 다님
if) Process 는 끝났는데 PCB는 queue에서 못나옴..
> 좀비 프로세스
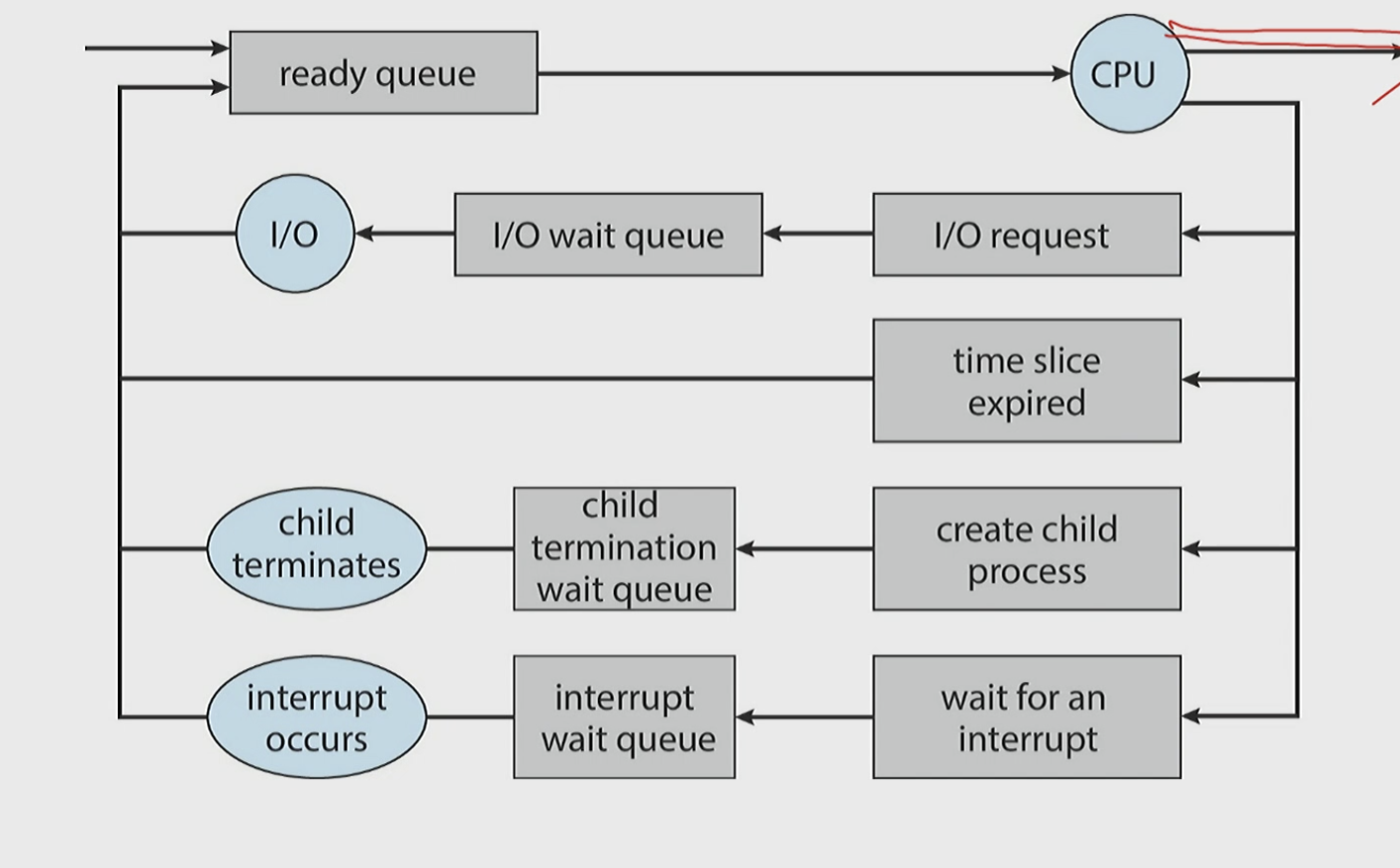
Scheduling Queue
: 1 program -> multiple process -> multiple queue 에 담아둠
>
ready -> CPU
준비가 된 Process들을
> I/O, time expired, child process 생성, interrupt 대기 등 wait queue에 넣고 일 시킬 준비
> 완료후 다시 ready
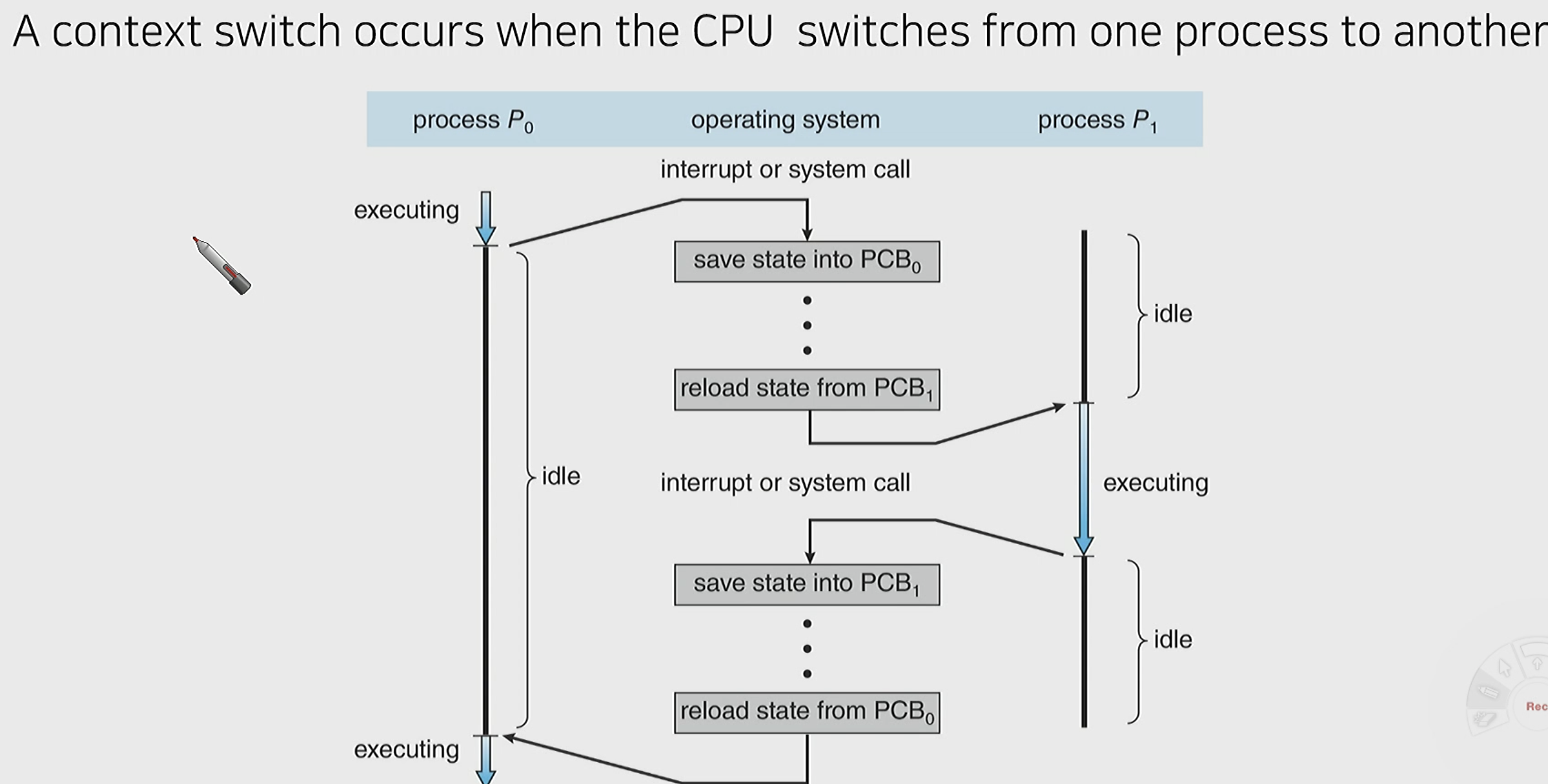
Context switching : 현재(save) -> 다음(reload)
// idle : 동작X ,휴식
PCB0 > interrupt/system call > PCB1